Trigger Point Therapy | Tibialis Anterior | Anatomy

The tibialis anterior trigger point typically causes pain in the front of the shin, ankle and on the big toe
The pain in the big toe can often be mistaken for gout, and the metabolic condition that causes gout may also irritate the trigger points in the lower leg muscles.
In most cases however, these trigger points are related to sports/overuse issues, and are often present in long distance drivers.
[Latin tibia, pipe or ute/shinbone; anterior, before]
ORIGIN
Lateral condyle of tibia. Upper half of lateral surface of tibia. Interosseous membrane.
INSERTION
Medial and plantar surface of medial cuneiform bone. Base of 1st metatarsal.
ACTION
Dorsi flexes ankle joint. Inverts foot. Antagonists: bularis longus, gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris, tibialis posterior.
NERVE
Deep peroneal nerve, L4, 5, S1.
BASIC FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT
Example: walking and running (helps prevent foot from slapping onto ground after heel strikes; lifts foot clear of ground as leg swings forward).
How to Massage the Tibialis Anterior
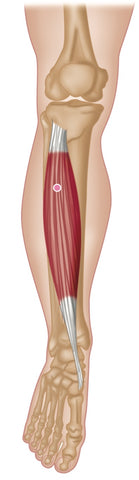
Tibialis Anterior - Common Trigger Point Site

Tibialis Anterior - Typical Referred Pattern
TRIGGER POINT REFERRED PAIN PATTERNS
Anteromedial vague pain along shin, with zone of pain 3–5 cm in ankle joint (anterior), culminating in great-toe pain (whole toe).
INDICATIONS
Ankle pain/tenderness, pain in great toe, shin splints (anterior tibial compartment syndrome), foot dragging, ankle weakness (children), gout toe, turf toe, falls, balance issues.
CAUSES
Direct trauma, twisted ankle, ill-fitting boots/shoes, poor orthotics, walking on uneven surfaces, stubbing great toe, overload (e.g. walking, car pedals).
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Lumbar discopathy. Arthritic toes. Anterior tibial compartment syndrome. Shin splints (anterior). Varicose veins. Gout.
CONNECTIONS
Extensor hallucis longus, peroneus tertius, extensor hallucis brevis, extensor digitorum brevis/longus, flexor hallucis longus, 1st dorsal interosseous.

Self Help - Pressure tools can be useful but be aware of varicose veins
GENERAL ADVICE TO PATIENTS
Self-massage techniques can be helpful. Be careful if there are varicose veins. Balls, hooks, and pressure tools can generally be used, as the muscle is fairly superficial.
Avoid long car journeys and use of pedals. Regularly change running surface/ shoes. Avoid walking (prolonged) on sloping surfaces.
Have stretch program (heat/warmth/cold). Adjust car seat. Use wedge under heel of foot for car pedal.
Links
Treating Ankle Sprains - Trigger Point Therapy
More Articles About Trigger Points
Certify as a Trigger Point Therapist

EDUCATION MEMBERSHIP PLANS
UNLIMITED ACCESS
FROM $19.95/monthly

Trigger Point Therapy Diploma Course

Clinical Reasoning and Assessment for Manual Therapists
This trigger point therapy blog is intended to be used for information purposes only and is not intended to be used for medical diagnosis or treatment or to substitute for a medical diagnosis and/or treatment rendered or prescribed by a physician or competent healthcare professional. This information is designed as educational material, but should not be taken as a recommendation for treatment of any particular person or patient. Always consult your physician if you think you need treatment or if you feel unwell.
About Niel Asher Education
Niel Asher Education (NAT Global Campus) is a globally recognised provider of high-quality professional learning for hands-on health and movement practitioners. Through an extensive catalogue of expert-led online courses, NAT delivers continuing education for massage therapists, supporting both newly qualified and highly experienced professionals with practical, clinically relevant training designed for real-world practice.
Beyond massage therapy, Niel Asher Education offers comprehensive continuing education for physical therapists, continuing education for athletic trainers, continuing education for chiropractors, and continuing education for rehabilitation professionals working across a wide range of clinical, sports, and wellness environments. Courses span manual therapy, movement, rehabilitation, pain management, integrative therapies, and practitioner self-care, with content presented by respected educators and clinicians from around the world.
Known for its high production values and practitioner-focused approach, Niel Asher Education emphasises clarity, practical application, and professional integrity. Its online learning model allows practitioners to study at their own pace while earning recognised certificates and maintaining ongoing professional development requirements, making continuing education accessible regardless of location or schedule.
Through partnerships with leading educational platforms and organisations worldwide, Niel Asher Education continues to expand access to trusted, high-quality continuing education for massage therapists, continuing education for physical therapists, continuing education for athletic trainers, continuing education for chiropractors, and continuing education for rehabilitation professionals, supporting lifelong learning and professional excellence across the global therapy community.

Continuing Professional Education
Looking for Massage Therapy CEUs, PT and ATC continuing education, chiropractic CE, or advanced manual therapy training? Explore our evidence-based online courses designed for hands-on professionals.


















