Treating the Hamstrings - A Common Sports Injury

Hamstring Injury
Ultimately, the hamstrings are trying to be gluteal muscles, while the lumbar muscles are trying to be hamstrings
The hamstrings eccentrically contract during gait in order to decelerate extension of the knee joint and hip flexion, while also playing a very important role in pelvic stability.
The hamstring muscles decelerate internal rotation on heel-strike.
The hamstrings disappear under the gluteus maximus and provide force closure of the sacroiliac joint through the coupled action of the force provided by the contralateral latissimus dorsi.
This force is transmitted through the sacrotuberous ligament and further up to the thoracolumbar fascia.
Massage Cupping for Tight Hamstrings - Vicki Ramsdell
Hamstring trigger points are often mistaken for sciatic pain
Typically, pain from trigger points is referred up toward the gluteal muscles, with some residual pain spreading down just below and behind the knee into the medial gaster of the gastrocnemius.
This pain can often be mistaken for sciatic pain. Weak inhibited gluteal muscles, including the gluteus medius, can lead to myofascial trigger points forming in the hamstrings and lumbar erector muscles, including the quadratus lumborum.
Ultimately, the hamstrings are trying to be gluteal muscles, while the lumbar muscles are trying to be hamstrings.
Hamstrings - Trigger Point Anatomy
It's easy for one or more of the hamstrings to get overloaded and just about anyone who plays sport regularly, from professionals to weekend warriors, should benefit from therapy in this area to help avoid what can become painful and long term injuries.
We generally take a look at the hamstrings on just about every client who plays a sport regularly that involves running, jumping and turning ..... even when there are no symptoms.
Fortunately, identifying and treating trigger points in the hamstrings is pretty straightforward although bear in mind that trigger points in large muscles will often require additional pressure.
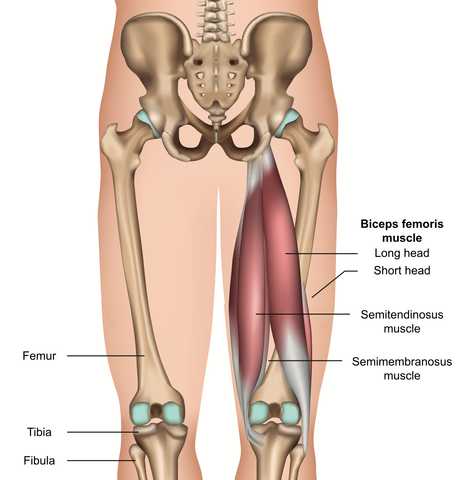
Hamstrings Muscles
Anatomy
The hamstrings consist of three muscles. From medial to lateral they are the semimembranosus, semitendinosus, and biceps femoris.
Origin
Ischial tuberosity (sitting bone). Biceps femoris also originates from back of femur.
Insertion
Semimembranosus: back of medial condyle of tibia (upper side part of tibia).
Semitendinosus: upper medial surface of shaft of tibia.
Biceps femoris: lateral side of head of bula. Lateral condyle of tibia.
Action
Flex knee joint. Extend hip joint. Semimembranosus and semitendinosus also medially rotate (turn in) lower leg when knee is flexed.
Biceps femoris laterally rotates (turns out) lower leg when knee is flexed.
Antagonists: quadriceps.
Nerve
Branches of sciatic nerve, L4, 5, S1, 2, 3.
Basic Functional Movement
During running, the hamstrings slow down the leg at the end of its forward swing and prevent the trunk from flexing at the hip joint.
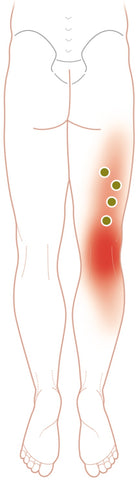
Biceps Femoris - Typical Referred Pain Pattern
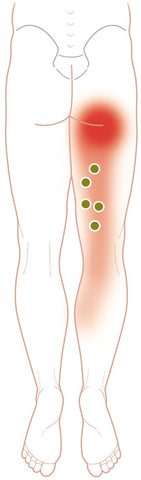
Semimembranosus/ Semitendinosus - Typical Referred Pain Pattern
Trigger Point Referred Pain Patterns
Semimembranosus and semitendinosus: strong 10 cm zone of pain, inferior gluteal fold, with diffuse pain posteromedial legs to Achilles tendon area.
Biceps femoris: diffuse pain posteromedial legs, with strong 10 cm zone posterior to knee joint.
Indications
Posterior thigh pain sitting/walking (worse at night), tenderness in back of legs may cause limping, pain worse on sitting, post back surgery, hamstring pain cycling/soccer/ basketball/tennis/football.
Causes
Prolonged driving, improper sitting/ work chair that digs into back of thighs, hip surgery, sitting cross- legged, hip/knee/ankle injury/ fracture, leg casts, high-heeled shoes, PSLE, sacroiliac joint dysfunction, improper stretching before/after sport.
Differential Diagnosis
Sciatica. Radiculopathy. Muscle tears. Osteitis. Bursitic osteoarthritis of knee. Knee joint dysfunction. Tenosynovitis.
Connections
Piriformis, popliteus, gluteal muscles, obturator internus, vastus lateralis, plantaris, gastrocnemius, thoracolumbar paraspinal muscles.
Self Help
Trigger points in hamstrings often occur from improper stretching before and after sports. It is very important to get the stretching techniques down pat. Balls and foam rollers can be very good for relieving pain and stiffness when you are at home.
Trigger Point Treatment Techniques
| Spray and Stretch | YES |
| Deep Stroking Massage | YES |
| Compression | YES |
| Muscle Energy Techniques | YES |
| Positional Release | YES |
| Dry Needling | YES |
| Wet Needling | YES |
About Niel Asher Education
Niel Asher Education (NAT Global Campus) is a globally recognised provider of high-quality professional learning for hands-on health and movement practitioners. Through an extensive catalogue of expert-led online courses, NAT delivers continuing education for massage therapists, supporting both newly qualified and highly experienced professionals with practical, clinically relevant training designed for real-world practice.
Beyond massage therapy, Niel Asher Education offers comprehensive continuing education for physical therapists, continuing education for athletic trainers, continuing education for chiropractors, and continuing education for rehabilitation professionals working across a wide range of clinical, sports, and wellness environments. Courses span manual therapy, movement, rehabilitation, pain management, integrative therapies, and practitioner self-care, with content presented by respected educators and clinicians from around the world.
Known for its high production values and practitioner-focused approach, Niel Asher Education emphasises clarity, practical application, and professional integrity. Its online learning model allows practitioners to study at their own pace while earning recognised certificates and maintaining ongoing professional development requirements, making continuing education accessible regardless of location or schedule.
Through partnerships with leading educational platforms and organisations worldwide, Niel Asher Education continues to expand access to trusted, high-quality continuing education for massage therapists, continuing education for physical therapists, continuing education for athletic trainers, continuing education for chiropractors, and continuing education for rehabilitation professionals, supporting lifelong learning and professional excellence across the global therapy community.

Continuing Professional Education
Looking for Massage Therapy CEUs, PT and ATC continuing education, chiropractic CE, or advanced manual therapy training? Explore our evidence-based online courses designed for hands-on professionals.


















