Understanding Herniated and Bulging Discs: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Herniated discs and bulging discs are common spinal conditions that can cause significant pain and discomfort. These conditions affect the intervertebral discs, which act as cushions between the vertebrae of the spine. While they share similarities, there are key differences between the two conditions, and understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management.
Herniated Discs:
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, occurs when the inner, gel-like nucleus of the disc protrudes through the tough outer layer, known as the annulus fibrosus. This protrusion can irritate nearby spinal nerves, leading to symptoms such as:
- Radiating pain, numbness, or tingling in the arms or legs (depending on the location of the herniation)
- Muscle weakness
- Difficulty with balance or coordination
- Loss of bladder or bowel control (in severe cases)
Herniated discs commonly occur due to age-related degeneration of the discs, trauma or injury to the spine, or repetitive stress on the spine from activities such as heavy lifting or improper lifting techniques. Treatment for herniated discs may include:
- Pain management strategies such as rest, ice or heat therapy, and over-the-counter or prescription medications
- Physical therapy to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine and improve flexibility
- Epidural steroid injections to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain
- Surgical intervention in cases where conservative treatments have been ineffective or if there is severe nerve compression requiring immediate attention
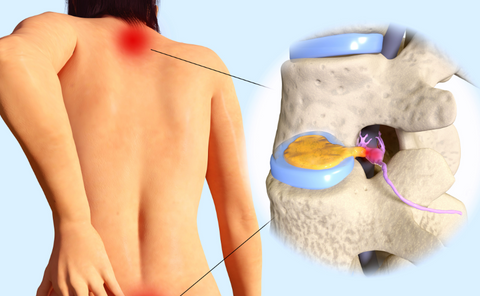
Bulging Discs:
A bulging disc occurs when the outer layer of the disc weakens or becomes damaged, causing the disc to protrude beyond its normal boundaries without rupturing. While similar to a herniated disc, a bulging disc typically does not cause symptoms unless it compresses nearby spinal nerves. Symptoms of a bulging disc may include:
- Localized back or neck pain
- Pain, numbness, or tingling that radiates into the arms or legs
- Muscle weakness or stiffness
Bulging discs often result from age-related changes in the spine, such as decreased disc height and elasticity, but they can also be caused by traumatic injury or repetitive strain. Treatment for bulging discs may involve:
- Similar conservative treatments as those for herniated discs, such as rest, physical therapy, and pain management techniques
- Minimally invasive procedures, such as spinal decompression therapy or nerve root injections, to relieve pressure on the affected nerves
- Surgical intervention in severe cases or if conservative treatments fail to provide relief
Comprehensive Approaches for Relieving Symptoms of Herniated or Bulging Discs: Integrating Natural Modalities
Managing symptoms of herniated or bulging discs often involves a multifaceted approach that combines conventional medical interventions with complementary and alternative therapies. Incorporating natural modalities such as trigger point therapy, massage therapy, cupping, and other conservative treatments can help alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and promote healing while minimizing the need for invasive procedures or medications. Let's explore how these modalities can be integrated into a holistic treatment plan for individuals with spinal disc issues:
1. Trigger Point Therapy: Trigger point therapy involves applying pressure to specific points in the muscles, known as trigger points, to alleviate pain and tension. For individuals with herniated or bulging discs, trigger point therapy can help target muscular imbalances and alleviate secondary muscle spasms that contribute to pain and discomfort. By releasing tension in the surrounding muscles, trigger point therapy can reduce pressure on the affected discs and improve overall spinal alignment.
2. Massage Therapy: Massage therapy offers a non-invasive and drug-free approach to managing symptoms of herniated or bulging discs. Therapeutic massage techniques, such as Swedish massage, deep tissue massage, and myofascial release, can help increase circulation, reduce muscle tension, and promote relaxation. Massage therapy can also target specific areas of pain and discomfort, providing targeted relief to individuals with spinal disc issues. Additionally, massage therapy can enhance the effectiveness of other treatments, such as physical therapy or chiropractic adjustments, by preparing the muscles and soft tissues for manipulation and mobilization.
3. Cupping Therapy: Cupping therapy has gained recognition for its ability to alleviate pain and promote healing in individuals with musculoskeletal conditions, including herniated or bulging discs. By creating suction on the skin, cupping therapy helps increase blood flow, reduce inflammation, and release tension in the muscles and soft tissues surrounding the affected discs. Cupping therapy can be particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing radiating pain or muscle spasms associated with spinal disc issues. When integrated into a comprehensive treatment plan, cupping therapy can provide symptomatic relief and support the body's natural healing processes.
4. Chiropractic Care: Chiropractic adjustments, or spinal manipulation, are commonly used to address misalignments of the spine and relieve pressure on the discs and nerves. By gently realigning the vertebrae, chiropractic adjustments can improve spinal function, reduce pain, and restore mobility. Chiropractors may also incorporate other modalities, such as spinal decompression therapy, electrical stimulation, or ultrasound, to complement adjustments and enhance treatment outcomes.
5. Acupuncture: Acupuncture is an ancient healing practice that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to promote balance and restore health. For individuals with herniated or bulging discs, acupuncture can help alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and improve circulation. Acupuncture may also stimulate the release of endorphins, the body's natural pain-relieving chemicals, providing long-lasting relief from symptoms.
6. Yoga and Exercise Therapy: Yoga and exercise therapy can play a crucial role in managing symptoms of herniated or bulging discs by strengthening the muscles supporting the spine, improving flexibility, and promoting proper posture. Gentle yoga poses and targeted exercises can help alleviate pain, reduce muscle tension, and improve overall spinal health. Additionally, yoga and exercise therapy can enhance mobility, stability, and functional capacity, enabling individuals to engage in daily activities with greater ease and confidence.
7. Nutritional Support and Lifestyle Modifications: Optimizing nutrition and making lifestyle modifications can support the body's natural healing processes and promote spinal health. Eating a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, staying hydrated, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking can all contribute to improved outcomes for individuals with herniated or bulging discs. Additionally, adopting ergonomic principles, practicing good posture, and incorporating stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation or mindfulness, can help minimize strain on the spine and reduce the risk of exacerbating symptoms.
Conclusion: By integrating natural modalities such as trigger point therapy, massage therapy, cupping, and other conservative treatments into a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals with herniated or bulging discs can find relief from pain and discomfort while supporting the body's natural healing processes. These holistic approaches offer non-invasive and drug-free alternatives to conventional medical interventions, empowering individuals to take an active role in their health and well-being. As always, it's essential to consult with qualified healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses individual needs and preferences. With a proactive and integrated approach, individuals with spinal disc issues can achieve improved function, mobility, and quality of life.
P.S. Why Are We Taller in the Morning?
The phenomenon of being taller in the morning is attributed to the natural process of spinal decompression that occurs during sleep. Throughout the day, gravitational forces compress the intervertebral discs, causing them to lose water content and height. During sleep, the body assumes a horizontal position, allowing the discs to rehydrate and regain some of their lost height. As a result, the spine elongates slightly, leading to a temporary increase in height upon waking.
Additionally, the muscles supporting the spine relax during sleep, further facilitating spinal decompression and elongation. However, as the day progresses and gravitational forces once again act on the spine, the discs gradually lose water content and height, causing a slight reduction in overall height by the end of the day.
In conclusion, herniated and bulging discs are common spinal conditions that can cause pain and discomfort, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, many individuals can find relief and improve their quality of life. Additionally, understanding the natural processes of spinal decompression, such as those that occur during sleep, can provide insights into our daily experiences of height variation and contribute to our overall understanding of spinal health and function.




















