Low Back Pain | Key Structures | Facet Joint Syndromes

The facet joint is highly innervated with pain receptors, making it susceptible to producing back pain
Lumbar Facet Joints and Low Back Pain
Anatomy
The facet joints in the vertebral column are located posterior to the vertebral body, and their role is to assist the spine in performing movements such as flexion, extension, side-bending, and rotation.
Depending on their location and orientation, the facet joints will allow certain types of motion but restrict others.
For example, the lumbar spine is limited in rotation, but flexion and extension are freely permitted. In the thoracic spine, rotation and flexion are freely permitted; extension, however, is limited by the facet joints (but also by the ribs).
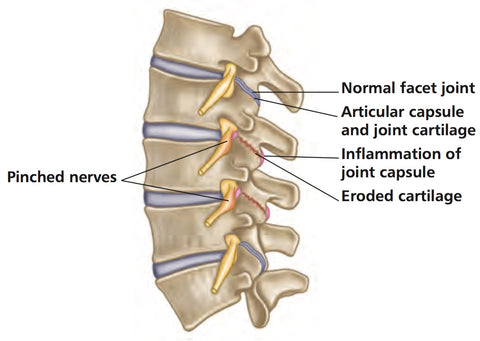
Facet Joint Syndrome is a common cause of Chronic Back Pain
Degeneration
Each individual vertebra has two facet joints: the superior articular facet, which faces upward and works similar to a hinge, and the inferior articular facet located below it. The L4 inferior facet joint, for example, articulates with the L5 superior facet joint.
Like all other synovial joints located in the body, each facet joint is surrounded by a capsule of connective tissue and produces synovial fluid to nourish and lubricate the joint.
The surfaces of the joint are coated with cartilage, which helps each joint to move (articulate) smoothly. The facet joint is highly innervated with pain receptors, making it susceptible to producing back pain.
Facet joints have a tendency to slide over each other, so they are naturally in constant motion with the spine and, like all types of weight-bearing joint, they can simply wear out and start to degenerate over time.
When facet joints become irritated (the cartilage can even tear), this will cause a reaction of the bone of the joint underneath the facet joint to start producing osteophytes, leading to facet joint hypertrophy, which is the precursor of facet joint disease/syndrome.
This type of syndrome or disease process is very common in many patients presenting with chronic back pain.
Treatment
To break up a cycle of recurring, acute facet joint pain, a number of treatments can be used successfully including trigger point therapy.
Facet Joint Syndrome (FJS) is often associated with trigger points in the multifidus muscles.
These muscles consists of a number of fleshy and tendinous fasciculi, which fill up the groove on either side of the spinous processes of the vertebrae, from the sacrum to the axis.
Treating trigger points in multifidus can often help provide relief to the chronic back pain that is a symptom of FJS.
In most cases, successful long-term treatment involves proper exercises, with instruction by a trained manual therapist or other healthcare provider.
Posture
Good posture (maintaining a normal curvature of the spine such as pulling the car seat quite forward or when standing at a sink, putting one foot up on a ledge, bending that knee a bit), support to the low back when seated or riding in a car (particularly in the acute phase).
A very useful posture when standing or sitting is the pelvic tilt, where one pinches together the buttocks and rotates forward the lower pelvis, and holding that position for several seconds, done several times per day.
Your therapist or healthcare provider should be able to advise on posture exercises that are suitable for you.
Fusion Massage for Tension Headaches
Dry Needling for Trigger Points
Certify as a Trigger Point Therapist
NAT Education Membership Plans

NAT TRIGGER POINT THERAPY DIPLOMA COURSE
EDUCATION MEMBERSHIP PLANS
UNLIMITED ACCESS
FROM $19.95/monthly
This trigger point therapy blog is intended to be used for information purposes only and is not intended to be used for medical diagnosis or treatment or to substitute for a medical diagnosis and/or treatment rendered or prescribed by a physician or competent healthcare professional. This information is designed as educational material, but should not be taken as a recommendation for treatment of any particular person or patient. Always consult your physician if you think you need treatment or if you feel unwell.
About Niel Asher Education
Niel Asher Education (NAT Global Campus) is a globally recognised provider of high-quality professional learning for hands-on health and movement practitioners. Through an extensive catalogue of expert-led online courses, NAT delivers continuing education for massage therapists, supporting both newly qualified and highly experienced professionals with practical, clinically relevant training designed for real-world practice.
Beyond massage therapy, Niel Asher Education offers comprehensive continuing education for physical therapists, continuing education for athletic trainers, continuing education for chiropractors, and continuing education for rehabilitation professionals working across a wide range of clinical, sports, and wellness environments. Courses span manual therapy, movement, rehabilitation, pain management, integrative therapies, and practitioner self-care, with content presented by respected educators and clinicians from around the world.
Known for its high production values and practitioner-focused approach, Niel Asher Education emphasises clarity, practical application, and professional integrity. Its online learning model allows practitioners to study at their own pace while earning recognised certificates and maintaining ongoing professional development requirements, making continuing education accessible regardless of location or schedule.
Through partnerships with leading educational platforms and organisations worldwide, Niel Asher Education continues to expand access to trusted, high-quality continuing education for massage therapists, continuing education for physical therapists, continuing education for athletic trainers, continuing education for chiropractors, and continuing education for rehabilitation professionals, supporting lifelong learning and professional excellence across the global therapy community.

Continuing Professional Education
Looking for Massage Therapy CEUs, PT and ATC continuing education, chiropractic CE, or advanced manual therapy training? Explore our evidence-based online courses designed for hands-on professionals.



















