Palmaris Longus - Trigger Point Therapy

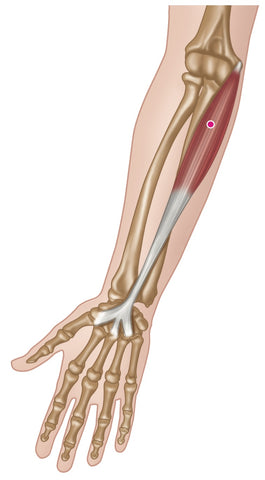
Palmaris Longus Muscle
Median Nerve Stretch
Pain from Palmaris Longus Trigger Points is typically experienced as a needle-like sensation
The Palmaris Longus decelerates extension of the hand at the wrist while decelerating supination of the hand against gravity and extension of the forearm at the elbow.
A focal point of pain from the palmaris longus is experienced as a needle-like sensation, rather than the deep aching pain of myofascial trigger points in many other muscles.
Pain can extend to the base of the thumb and the distal crease of the palm. A residue of this pain can travel to the distal volar forearm.
Part of the superficial layer, which also includes the pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, and flexor carpi ulnaris.
The palmaris longus muscle is absent in 13% of the population.
Palmaris Longus - Common Trigger Point Site
Origin
Common flexor origin on anterior aspect of medial epicondyle of humerus.
Insertion
Superficial (front) surface of flexor retinaculum and apex of palmar aponeurosis.
Action
Flexes wrist. Tenses palmar fascia.
Antagonists: extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi ulnaris.
Nerve
Median nerve, C(6), 7, 8, T1.
Basic Functional Movement
Examples: grasping a small ball; cupping palm to drink from hand.

Palmaris Longus Trigger Points - Typical Referred Pain Pattern
Trigger Point Referred Pain Patterns
Diffuse pain in anterior forearm; intense pain zone 2–3 cm in palm of hand, surrounded by a superficial zone of prickling and needle-like sensations.
Indications
Pain and “soreness” in palm of hand, tenderness in hand/palm, functional loss of power in grip, tennis elbow.
Causes
Direct trauma (e.g. fall on outstretched arm), occupational, racquet sports, digging in palm.
Differential Diagnosis
Neurogenic pain. Dupuytren’s contracture. Carpal tunnel syndrome. Complex regional pain syndrome (reflex-sympathetic dystrophy). Scleroderma. Dermatomyositis.
Connections
Flexor carpi radialis, brachialis, pronator teres, wrist joints (carpals), often associated with middle head of triceps brachii.
Self Help
Self-massage techniques can be helpful, especially using balls.
Advice
Avoid prolonged “gripping,” especially of power tools. Stretching and heat. Regular breaks.
Trigger Point Treatment Techniques
| Spray and Stretch | YES |
| Deep Stroking Massage | YES |
| Compression | YES |
| Muscle Energy | YES |
| Positional Release | YES |
| Dry Needling | YES |
| Wet Needling | YES |
EDUCATION MEMBERSHIP PLANS
UNLIMITED ACCESS
FROM $19.95/monthly
About Niel Asher Education
Niel Asher Education (NAT Global Campus) is a globally recognised provider of high-quality professional learning for hands-on health and movement practitioners. Through an extensive catalogue of expert-led online courses, NAT delivers continuing education for massage therapists, supporting both newly qualified and highly experienced professionals with practical, clinically relevant training designed for real-world practice.
Beyond massage therapy, Niel Asher Education offers comprehensive continuing education for physical therapists, continuing education for athletic trainers, continuing education for chiropractors, and continuing education for rehabilitation professionals working across a wide range of clinical, sports, and wellness environments. Courses span manual therapy, movement, rehabilitation, pain management, integrative therapies, and practitioner self-care, with content presented by respected educators and clinicians from around the world.
Known for its high production values and practitioner-focused approach, Niel Asher Education emphasises clarity, practical application, and professional integrity. Its online learning model allows practitioners to study at their own pace while earning recognised certificates and maintaining ongoing professional development requirements, making continuing education accessible regardless of location or schedule.
Through partnerships with leading educational platforms and organisations worldwide, Niel Asher Education continues to expand access to trusted, high-quality continuing education for massage therapists, continuing education for physical therapists, continuing education for athletic trainers, continuing education for chiropractors, and continuing education for rehabilitation professionals, supporting lifelong learning and professional excellence across the global therapy community.

Continuing Professional Education
Looking for Massage Therapy CEUs, PT and ATC continuing education, chiropractic CE, or advanced manual therapy training? Explore our evidence-based online courses designed for hands-on professionals.



















